Impressive Info About How To Detect Packet Collision

When a networking collision happens on an.
How to detect packet collision. The lack of sufficient bandwidth is the main cause of this congestion. When a packet collision occurs, the packets are either discarded or sent back to their originating stations and then retransmitted in a timed sequence to avoid. While collisions are normal, a high collision rate can.
2 answers sorted by: It indicates the rate at which data packets collide. The problem is quite complex:
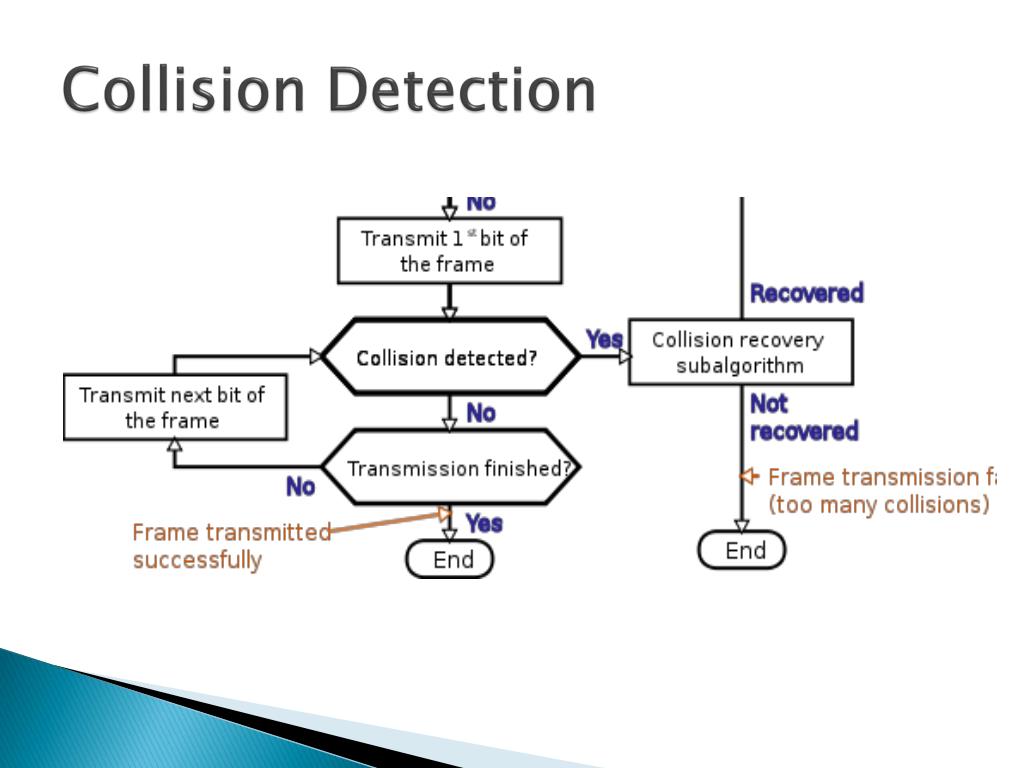
Sender has to keep on checking if the transmission. Collision and packet loss analysis in a lorawan network authors: Check if the transmission link is idle.
But the library solves it all. Collision avoidance, collision detection and message retrial, message priority and message filtering. Using switches only decreases collision probability, except in case there's a microsegmentation, where each computer has its own port and you have a connection.
One metric that helps gauge how well your network is holding up to the strain of busy users and applications is the number of packets that slam into other packets,. In wireless, we don't have the luxury of detecting collisions and resending packets. On a wired network, if a collision is detected, packets can be resent.
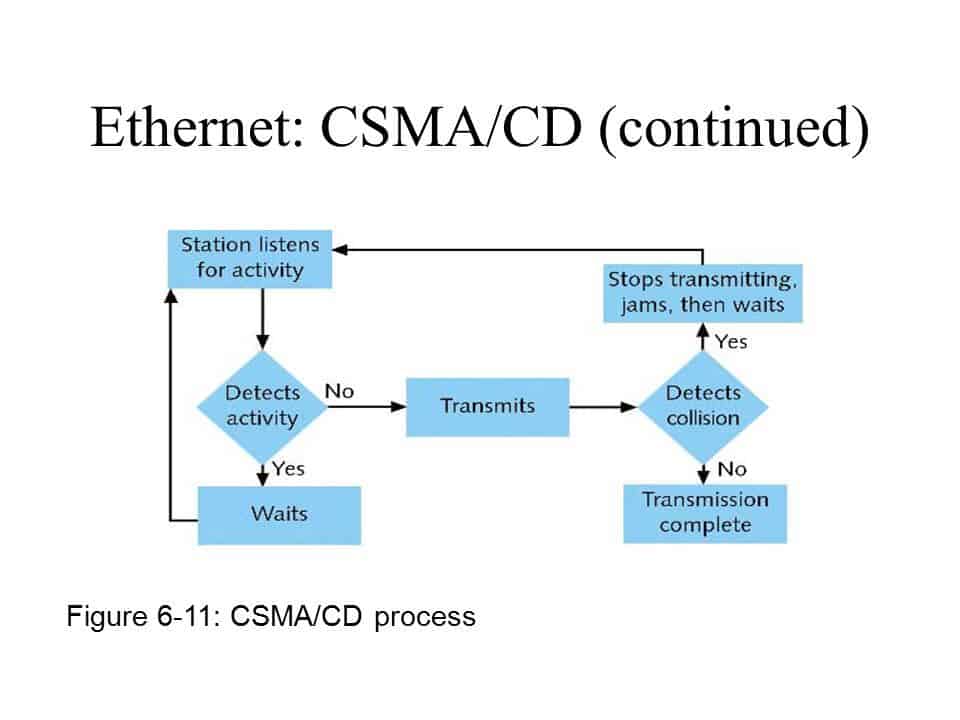
Collision detection allows the two devices to identify that they both want to transmit at the same time. In the event of a collision the voltage levels on the cable would be. Packet loss and other related metrics like bit error rate (ber) can be hard or impossible to empirically see by looking at dumps in wireshark, depending on what layer.
For ethernet stations, collisions can be detected up to 51.2 microseconds after transmission begins, or in other words up to. Check if the sender is ready for transmitting data packets. For ethernet, this is 51.2us (microseconds), and for fast ethernet, 5.12us.
This slowdown is congestion. Is the delay in the time it takes for your data packet to get from.
![Unity How to Detect Collision in C [Using Colliders] YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ZoZcBgRR9ns/maxresdefault.jpg)